I hope you’ll check out my books: Photographing Architecture and Understanding and Controlling Strobe Lighting
and Understanding and Controlling Strobe Lighting . I hope you’ll get copies if you haven’t already. Of course you know that one reason for this blog is to sell the book and get you to consider one of my classes at BetterPhoto.com: An Introduction to Photographic Lighting, Portrait Lighting on Location and in the Studio, Getting Started in Commercial Photography
. I hope you’ll get copies if you haven’t already. Of course you know that one reason for this blog is to sell the book and get you to consider one of my classes at BetterPhoto.com: An Introduction to Photographic Lighting, Portrait Lighting on Location and in the Studio, Getting Started in Commercial Photography


I was going to write about some more handy equipment in this issue, but I decided to put that off. I think I’ll be back to talking about stuff, particularly DIY stuff soon. I had breakfast with another experienced photographer, I don’t want to say old, a couple of days ago. We talked about some of the things we miss from the old days and both of us missed watching a print come up in a tray of developer. Whenever I talk about this with someone we end up using the word magic. When you put an exposed piece of silver gelatin paper into a tray of developer there is no picture, it’s just white paper. As you agitate the print in the developer the image slowly appears on the paper. If you’ve ever seen a Polaroid SX-70 print develop, it’s like that, only better. I know I’ve written about this stuff before, but I find it interesting and, well, magical.

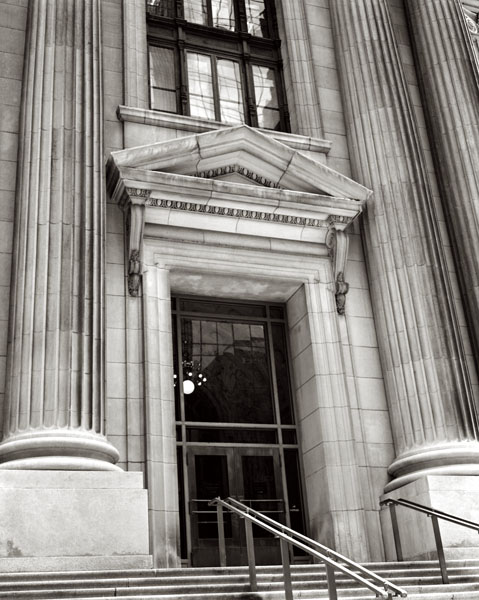
8.25 inch Gold Barrel Dagor on 8X10 film
Photography, before digital was mostly about magic goo. Like baking a cake you followed a recipe, and if everything was done properly, you got a picture. If everything was done well the picture would last. It’s been that way since William Henry Fox Talbot first made a paper negative. Fox Talbot used sodium chloride, table salt to make his images safe in daylight, so salt was the first magic goo. The thing is that few people really understood how the chemicals interacted, but a lot of us understood how to control what they did. Perhaps the person who understood the interaction best was C.E. K. Mees who ran Kodak Labs.

63mm Zeiss Luminar on 6X7cm film
I bring this up because, as I’ve mentioned before, I’m doing some personal work with my 8X10 Toyo camera. This brings me back into the land of magic goo. I’m testing different developers in an attempt to make a more perfect negative. I used Kodak chemicals, both HC-110 and, more recently, Xtol, to develop film for decades. Now, however, Kodak is imperiled, so I need to look for another supplier. It’s amazing how many things that I relied on Kodak for. At breakfast I discussed the Kodak Camel Hair brush with my friend. Kodak made things that couldn’t possibly have made a difference to their bottom line, but made a difference to photographers everywhere, like a good brush for cleaning film holders. I’ve been mixing a version of a Kodak developer, D-23. I got the recipe from The Darkroom Cookbook . Those of us working in the old ways are going to have to make a lot of things from scratch.
. Those of us working in the old ways are going to have to make a lot of things from scratch.

48cm Goerz Berlin Dogmar 8X10in. film
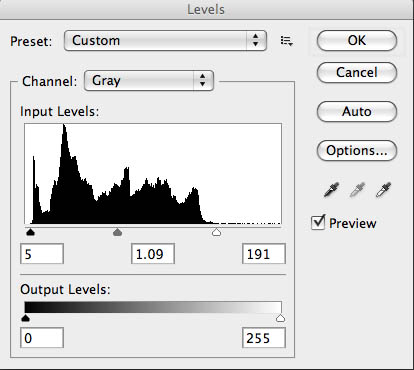
The problem is to know if everything is working well. Today I processed test negatives in D-23 and in Xtol. I’ve ordered some ID-11, an Ilford developer, and I’ll process a negative in that next week. I find that I do a lot of testing. I’ve mentioned before that a photographer needs to test equipment. If you don’t test you’ll never really know what you’re doing. Then you’ll not only believe in magic, you’re relying on magic that you don’t understand. I’ve attached copies of the negatives I processed in Kodak Xtol, they have a longer contrast range than the negs I did in D-23.

65mm Schneider Super Angulon 4X5in. film
Another magical area of large format photography is lenses. Although I’ve studied the physics and worked with the thin lens equations, I still find the way in which lenses bend light quite magical. At least as far back as 1840, when Joseph Petzval developed the first portrait lenses, people understood how much the lens affected the image. The goals of lens design, at least until the 1960s, were to make a lens that was sharp, had large coverage, even illumination, strong contrast and was fully corrected for spherical aberration and chromatic aberration and eliminated coma, unless you were trying to make a soft focus lens, in which case none of these might apply. It’s important to understand that you couldn’t, and still can’t, make a perfect lens: all lenses designs are compromises. But older lenses made different compromises so some are considered classic and others crap. I’ve always been very interested in lenses from Goerz and Schneider. I am pleased that I currently own two Goerz lenses, an 8 1/4 inch Dagor from the American version of Goerz and a 48cm Dogmar that is from Berlin Goerz. I’ve already mentioned that I recently acquired a 14 inch Dagor that is a Schneider Dagor. The Schneider Dagors are the last of this noble design. I am also getting a lot of use from my older Schneider Angulon (actually it is old enough to be a Jos. Schneider & Co.) and I also use a wide angle G-Claron from the modern version of Schneider. Of course I also carry a bunch of diopters to create soft focus lenses, for more about these check out this article.

135mm Schenider Xenar 4X5in. film
The pictures this week are all large format images. I put the format and the lens name in the caption.

65mm Super Angulon 4X5in. film
I’m looking at apps for my phone that will help with metering and other aspects of large format photography. So far I’ve found that beeCam Lightmeter is interesting. If you have any suggestions let me know at john@siskinphoto. I’ll put up people suggestions in a future blog. By the way I’m using an android phone, but if you have a suggestion for an iPhone I’ll be happy to pass it along.
Please consider one of my classes at BetterPhoto.com:
An Introduction to Photographic Lighting
Portrait Lighting on Location and in the Studio
Getting Started in Commercial Photography
If you’re in the Indianapolis area there are other opportunities as well. I’ll be showing much of my personal architectural work in June at Indiana Landmarks. Please come look.